
RIGID Direct Expansion System
High temperatures are a huge enemy of electronic appliances. Elevated heat can cause damage and compromise performance. Depending on the damage severity, it could destroy the device and render it unusable. That's why you need reliable electronics cooling systems that can ensure your products continue functioning at optimal levels.
RIGID designed Direct Expansion System is a unique mini condensing unit for instruments or electronics cooling.
There is no need for a redundant coolant loop and that the refrigerant directly cools the desired payload via a cold plate. We'll tell you more about the system's specifics in this article. You'll also learn details about the direct expansion cooling systems, and why it's important to have active cooling!
What Is a Direct Expansion System?
Direct expansion systems in refrigeration systems have been growing rapidly because of their simplicity of construction, their ability to get rid of most ductwork and piping, and their ease of integration into the user's equipment. Nowadays direct expansion systems are widely used because the installation work becomes easier and reduces the cost of the entire system for the user.
A direct expansion system refers to an installation where the chiller is the part of customer's equipment and device you are cooling. The direct cooling system
is directly in contact with user's evaporators like a cold plate. In fact, with no secondary coolant needed, the system only requires minimal parts.
It is not necessary to circulate cool air or to circulate coolant with fans or pumps. Complexity and inefficiency are added by these additional components. Additional thermal resistance is induced by the second coolant (air or liquid) and it adds heat to the cooling system, reduces net cooling capacity.
It doesn't contain and evaporator, which minimizes the work around tubing and installation. You can integrate the chilling solution into your own design evaporator or heat exchangers, which is also a huge space saver.
Why You Should Choose a Direct Expansion System
Direct expansion (DX) is an excellent pick for electronics cooling. If you choose it for your application, you'll get the following benefits:
● It's easy to install. That minimizes the hassle but also the potential costs of installation.
● It minimizes required space. Instead of adding it as a separate component, you put the electronics cooling system as part of your device. Therefore, it doesn't take any additional room.
● Easy to adjust and maintain. You can set the system to the desired settings easily, especially if you use RIGID's solution. Our chiller allows you to pick the desired speed, which sets the desired temperature accordingly.
● Spending little energy. A mini chiller has the significant advantage of utilizing little energy. Since it is compact, it doesn't need as much energy as bigger devices. Premium mini cooling solutions have the same performance as larger alternatives. That means you'll still get the expected results while spending less on energy.
● A minimal noise level. RIGID understands that an electronics cooling fan can be noisy. That's why it worked hard on reducing the noise level to less than 40dB. That would be similar like you are talking to someone in a library by using a quiet voice.
How Does a Direct Expansion System Works for Chilling?
This system has multiple components, including a mini compressor, a condenser, a drive board, and a capillary and other refrigeration conponents. It's vital to note that you can expect chilling with our patent controller panel. Usually our standard product has only cooling. But if you use a reversible valve, it's possible for the cooler to work as a heating system, too. That increases the device's versatility and maximizes its value for money.
The flow control unit is in charge of expanding the refrigerant. RIGID has an electronics liquid cooling solution that includes a liquid refrigerant. The capillary tube or valve for thermal expansion serves for flow control.
If you check the compressor, you'll find the receiver after it. That's what serves for storing high-heat and high-pressure liquid refrigerant. From this component, there is a liquid path that the refrigerant follows to the thermal expansion valve.
The flow control reduces the liquid pressure to the pressure of the evaporator. The temperature that the liquid refrigerant has once it reaches the evaporator should be lower than the area it tries to cool down. Some liquid will vaporize to ensure the refrigerant reaches the desired temperature in the evaporator.
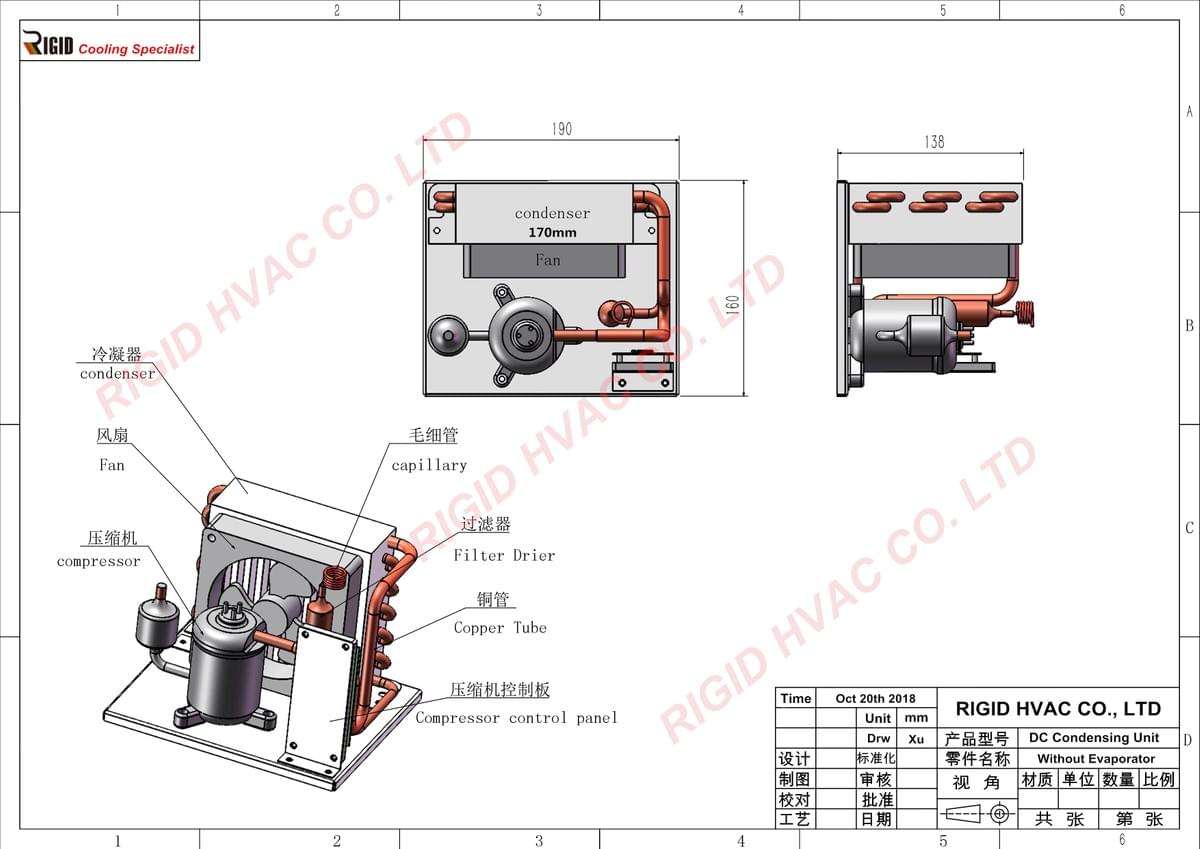
What Happens in the Evaporator Coil?
The next step involves the liquid vaporizing in the evaporator coil (Capillary). This component maintains a steady pressure and temperature. The heat goes through the evaporator's wall to the liquid that vaporizes. As time passes, more of the refrigerant vaporizes until it completely vaporizes. There's also no more moisture in the air. The evaporator coil condenses it.
If you look underneath the coil, you'll find a condensate pan. It will catch the water that drips down. From there, it moves the water to the drain. It's necessary to connect a tube or a hose that will ensure the water can reach the drain.
It's easier if the pan is below the water that's dripping. That way, you can let gravity do its job. But if the water has to go up to the condensate pan, you will need a pump. The pump will ensure the water goes up and reaches the drain. The reason you do this is to remove the humidity from the outside area.
The Compressor Starts Attracting the Vapor
Compressor is the most important component of an electronics cooling system. RIGID mini compressor is a key component to a refrigeration system, it is the “heart” of such appliances, comparable to a car engine or even the human heart. You'll find a suction inlet on this part. That inlet has a suction path where the vapor goes. So, the evaporator creates vapor, and then it goes to the compressor.
This part does the job of compressing the vapor. That way, it increases in pressure and temperature. The final step is the compressor discharging the vapor. It follows the discharge path designed when creating the entire system. The vapor proceeds into the condenser coil.
Why Active Cooling Systems Better Than Passive Cooling Options?
In product design, management of thermal conditions for maximum efficiency is a common issue, particularly in electronics cooling. To solve this challenge, we need to design microprocessors and printed circuit boards (PCBs) that use less energy and will not overheat.
In order to tackle issues that arise due to heat, engineers employ different cooling systems to manage the situation. It is possible to divide these cooling systems into two main categories: those with active cooling and those with passive cooling. But what is the difference between them?
The crucial difference is the temperature that these two systems can reach. If you use a passive cooling approach, the lowest point will be the ambient temperature. That means your electronics could reach the temperature of the room. However, there's no option for it to go lower than that. If you use an active cooling system, it will have extra energy. Think of it as a power electronics cooling solution that can reach the desired temperature that your device requires.
Let's talk about the working process of these two options!
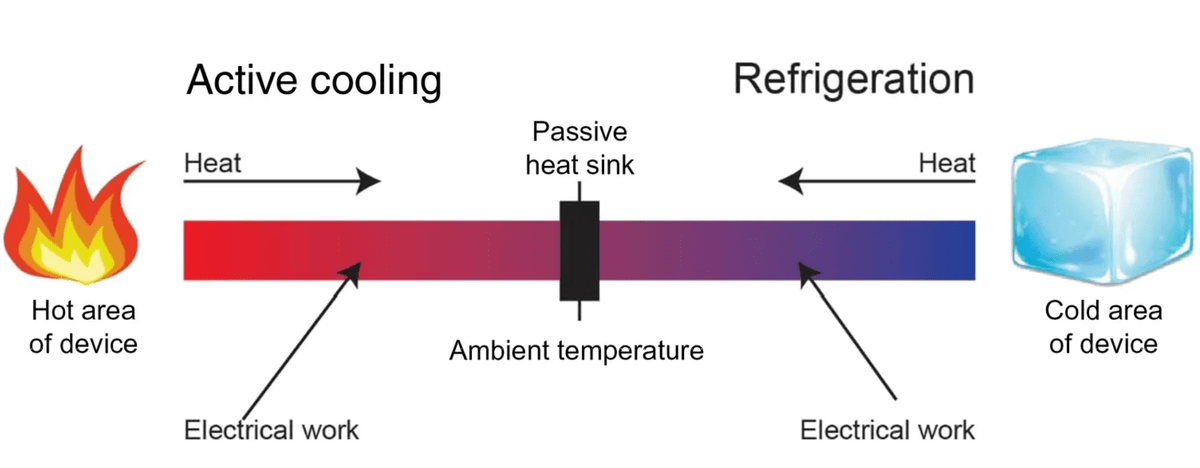
How Passive Cooling System Works?
These systems usually have ambient air as the ultimate heat sink in an enclosed interface. This interface will increase its temperature until it is hot enough to start releasing the heat into the nearby area. You can use various approaches, such as heat pipes, conductive chassis, and liquid coolant loops to decrease this temperature rise.
The problem is these devices won't deal with the thermal resistance that appears when the heat moves to the outside area. You can use fans, but only to decrease the enclosure surface to the heat level of the ambient air. That's why your electronics could reach heat levels above the ones recommended for their performance. It frequently happens if the temperature is high in the area.
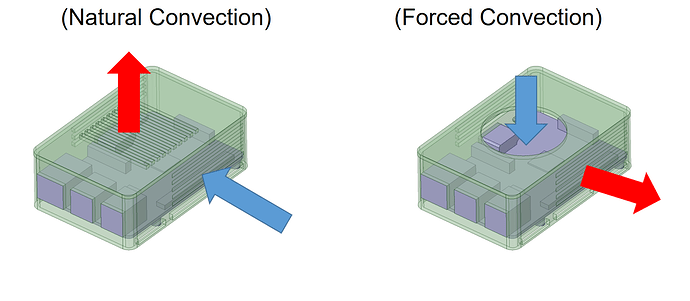
How Active Cooling Works?
These systems come with additional energy that helps to lower the heat to the desired level. They operate to decrease the temperature of any part that has air exposure. That way, they move more heat to the area. Subsequently, it reduces the temperature on the parts that are directly in touch with your device.
You can use different technologies for active cooling. If you are looking for an effective way that won't consume a lot of energy, vapor compression systems are your best bet. These are light, which means they won't add much extra weight to your product. Vapor compression doesn't consume a lot of energy, which makes it a smart and eco-friendly solution.
RIGID utilizes vapor compression in mini chiller systems. That allowed us to develop a unique solution that has versatile applications. Our mini cooler has become popular across various industries, and we are proud of that achievement!
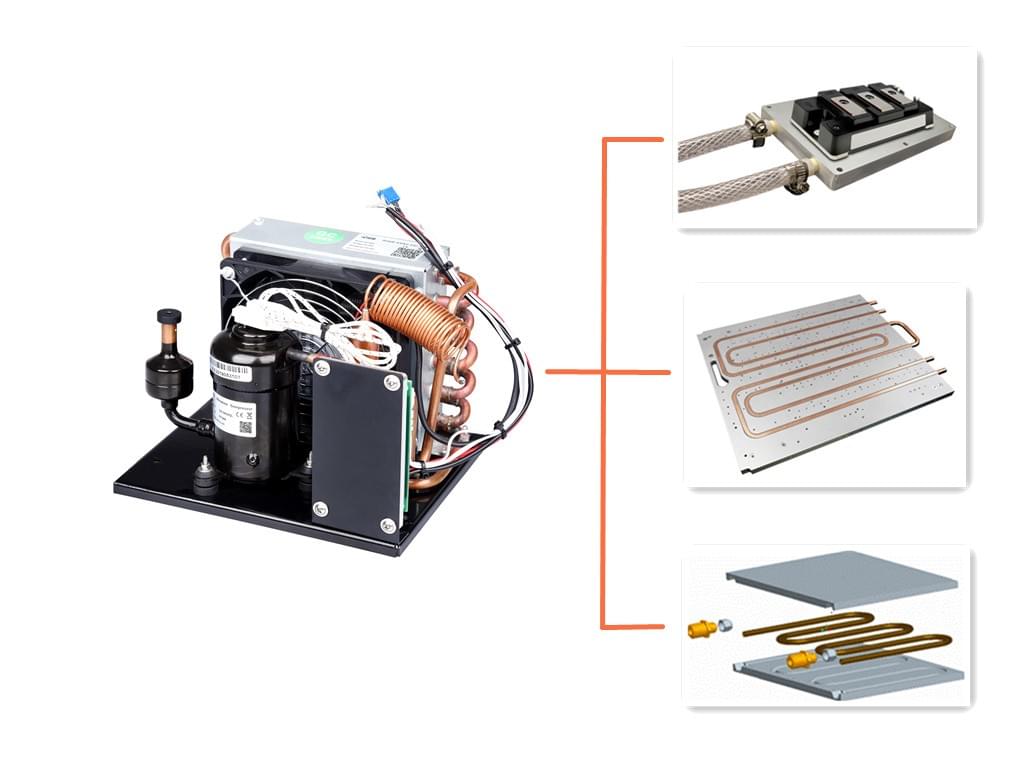
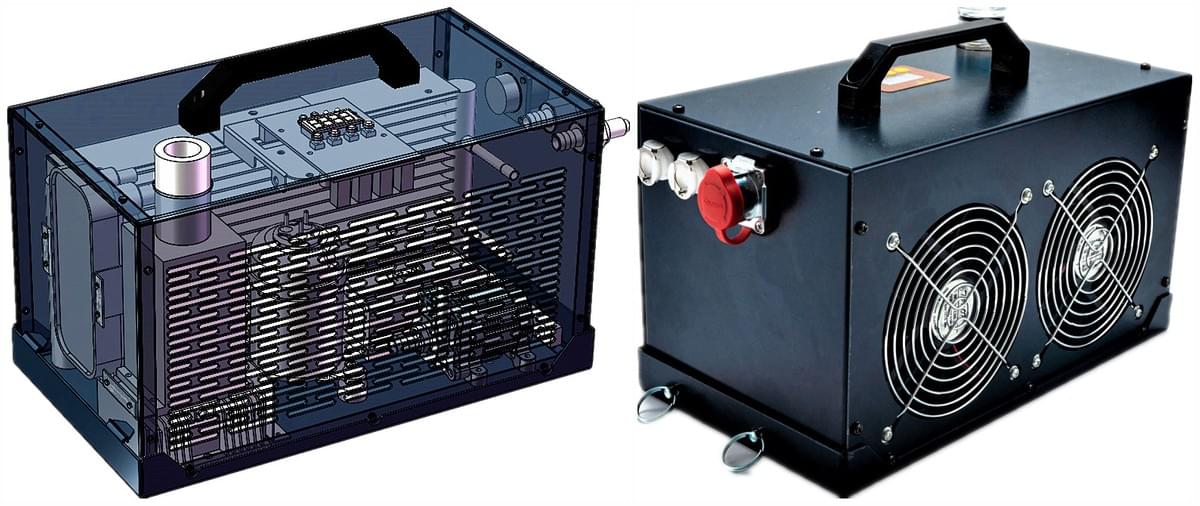
What You Should Know about RIGID's Other Compact Coolers
It is a light-and-lively mini cooling system. Less Weight. More Power. Minimal footprint with extraordinary cooling capacity. This compact cooler is a commercial off-the-shelf product. No Maintenance. No Ice. No Hassel. It can provide 24/7 continuously cooling in a hot environment. It's especially used to increase personal effectiveness in hot weather conditions or while using thicker protective equipment, markets include hospital, medical, military, firefighters, outdoor workers, 1st responders, and racing...
The compact cooler AlphaCooler is an active personal cooling system. It has been widely used by racing drivers to maintain normal body temperature when racing activities. It works by pumping a chilled fluid through a vest lined with a network of tubing, use a circulating chilled liquid as the cooling medium. Metabolic heat is transferred to the circulating liquid, which is pumped back to a cooling unit where the heat is rejected.
AlphaCooler is a commercial off-the-shelf product. No Ice. No Hassel. Full Power. It can provide 24/7 continuously cooling in a hot environment.
It is an active compressor-driven cooling unit. It works safely, rapidly, and efficiently. The coolant fluid is chilled by AlphaCooler, using miniature rotary vapor compression compressor cooling, and re-circulated back to the heat-transfer garment to continuously cool the user.


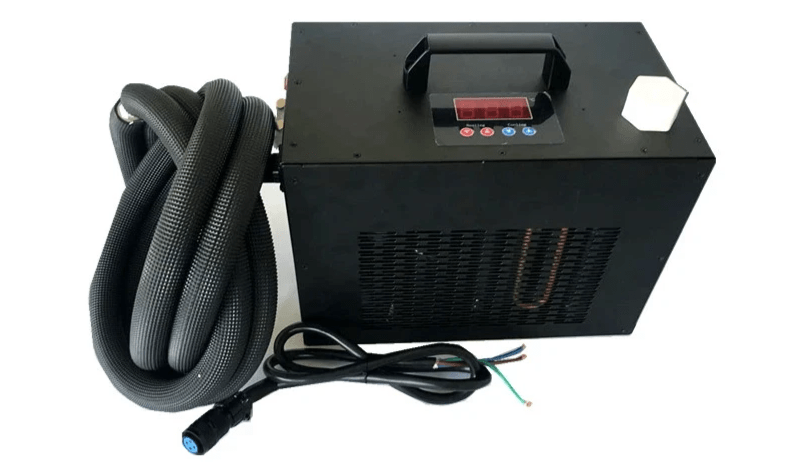
This 24V Small Liquid Cooler is not only our smallest cooling system, but as far as we know, it's the world's most compact liquid cooler option. Our chiller has an approximate size of 335x205x235 millimeters. That means it takes as little room as possible.
Apart from ensuring it's compact, we can also work with you to integrate the chiller directly into the product. That way, you won't waste a centimeter of space on the cooling system, and you'll still get impressive results. Apart from the small size, it's vital to mention that our chilling solution is light. It won't weigh more than a few pounds. That makes it an excellent choice for various electronics and different industries.
Here is an overview of the main features offered by RIGID 24V Liquid Cooler LC3220E-H:
● The available voltage is 24V. If you need an alternative that operates on 12V or 48V, don't hesitate to contact our experts.
● The system uses an R134A refrigerant. This is the most frequently used refrigerant across different cooling solutions.
● Dual functions of heating and cooling. The device can reduce and maintain a low temperature. If necessary, it can also act as a heater and increase the temperature to the desired level.
● Total control in your hands. You can use a digital display to adjust all settings to your requirements.
● Different capacities. The strength varies from 100W to 550W. It only depends on your requirements, and our team can suggest the most suitable solution for your needs.

What're Benefits of Using Mini Chiller Systems Designed by RIGID?
Why would you use our cold plate electronics cooling solutions? That's a good question, which is why we listed the main benefits of our systems below!
Versatility
If we say electronics, that's a term covering a wide range of devices. And wherever you have the need to cool down the device, you can use our chillers. They are suitable for medical applications, but also laser cooling, body treatment, and even personal cooling solutions. Our chilling solutions are already popular in a wide range of markets, from military and racing to home appliances and other industrial purposes.
Small, But Powerful
While we created our liquid chiller, we had a single thought in our mind. We wanted a powerful solution in a small package. The entire RIGID team worked to reduce the size of the cooler while not compromising its performance. We are proud that our solutions are tiny and efficient but deliver impressive and consistent results!
Extremely Quiet
Forget about those fans that disrupt your activities and don't allow you to focus on anything else. RIGID liquid coolers come with quiet fans, and the maximum noise of our devices is only 40dB. That's a level that will ensure you can stay focused on your tasks while the system is in operation.
Why RIGID Is the Right Partner for All Your Small Cooling Needs
RIGID was established over a decade ago. Our company had a different name when it was founded in 2010. It was in 2016 when we rebranded it to RIGID for the worldwide market.
Our goal was always simple – develop a solution that will suit even the most demanding clients' cooling needs. We invested years of research in developing a liquid cooler that's versatile, powerful, and compact. Today, we are proud of a product that revolutionized the Chinese and world markets. RIGID made sure to use high-quality components and offer exceptional quality while keeping affordable prices. We are proud that our products deliver the best value for money out there.
Do you need a liquid chiller for your electronics? If yes, we have a simple form that you can fill to submit an order. And if you have any questions, we can help you identify the best solution for your application. Feel free to contact us, and our team will respond to your inquiry in no more than 12 hours!
