Introduction

Cold plate technology has become a game-changer in various industries when it comes to efficient cooling solutions. But how does a cold plate work, and what sets it apart from traditional cooling methods? In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the inner workings of cold plates, exploring their purpose and function in modern applications.
Understanding the Basics of Cold Plate Technology
At its core, a cold plate is a passive heat exchanger that transfers thermal energy from one point to another using the principles of conduction. Cold plates effectively dissipate heat away from sensitive components or systems by utilizing a thermally conductive material such as aluminum or copper. This technology has revolutionized cooling solutions by providing an efficient and reliable method for managing heat in various applications.
Exploring the Inner Workings of Cold Plates
So, how do cold plates work exactly? Liquid cooling is a common method employed by cold plates, where a coolant circulates through internal channels to absorb heat from the source and dissipate it elsewhere. This process allows for precise temperature control and superior heat dissipation compared to traditional air cooling methods.
The Purpose and Function of Cold Plates
The primary function of cold plates is to maintain optimal operating temperatures for electronic components, medical equipment, automotive systems, and more. By efficiently removing excess heat generated during operation, cold plates ensure the reliability and longevity of critical systems while enhancing overall performance.
The Mechanics of Cold Plates
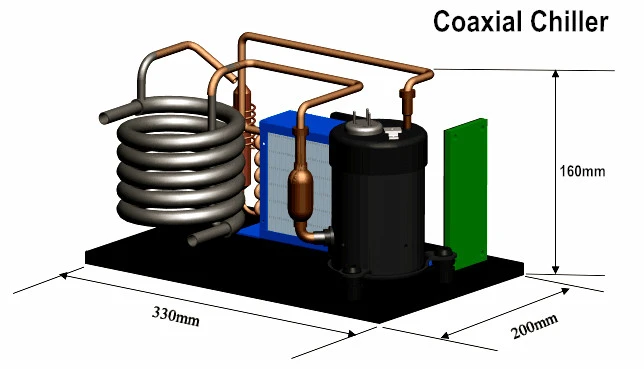
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Dissipation
Cold plates transfer heat away from a source using a coolant, typically water or other liquids with high thermal conductivity. The cold plate absorbs the heat and dissipates it through the coolant, which carries the heat away from the source to be released into the surrounding environment. This heat dissipation method is highly effective in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for electronic components, such as CPUs and GPUs in computers. By utilizing a liquid with high thermal conductivity, cold plates can efficiently transfer and dissipate heat, preventing overheating and potential damage to sensitive equipment.
Liquid Cooling vs. Air Cooling: A Comparative Analysis
Liquid cooling in cold plates is more efficient than air cooling due to liquids' higher thermal conductivity compared to air. This allows for faster heat dissipation and more effective temperature control, making liquid-cooled cold plates ideal for applications where precise temperature regulation is crucial.
Liquid cooling in cold plates also offers the advantage of operating at lower temperatures than air cooling systems. This is particularly beneficial for electronic components and other sensitive equipment that require a consistently low operating temperature to function optimally. By maintaining a lower temperature, liquid-cooled cold plates can help extend the lifespan of the equipment and reduce the risk of overheating-related malfunctions.
Design and Materials of Cold Plates
The design and materials of cold plates play a crucial role in their effectiveness. Cold plates are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, to facilitate efficient heat transfer. The design of the internal channels also impacts the flow and distribution of coolant, affecting the overall performance of the cold plate system.
Furthermore, the size and shape of the cold plate also impact its effectiveness, with larger plates providing more surface area for heat dissipation. In addition to traditional materials like copper and aluminum, newer cold plates may incorporate advanced materials such as graphite or composite to enhance thermal conductivity further and reduce weight. The choice of material and design must also consider the specific application and industry requirements, as different industries may have varying demands for thermal performance, corrosion resistance, or weight constraints.
Applications and Industries Utilizing Cold Plates
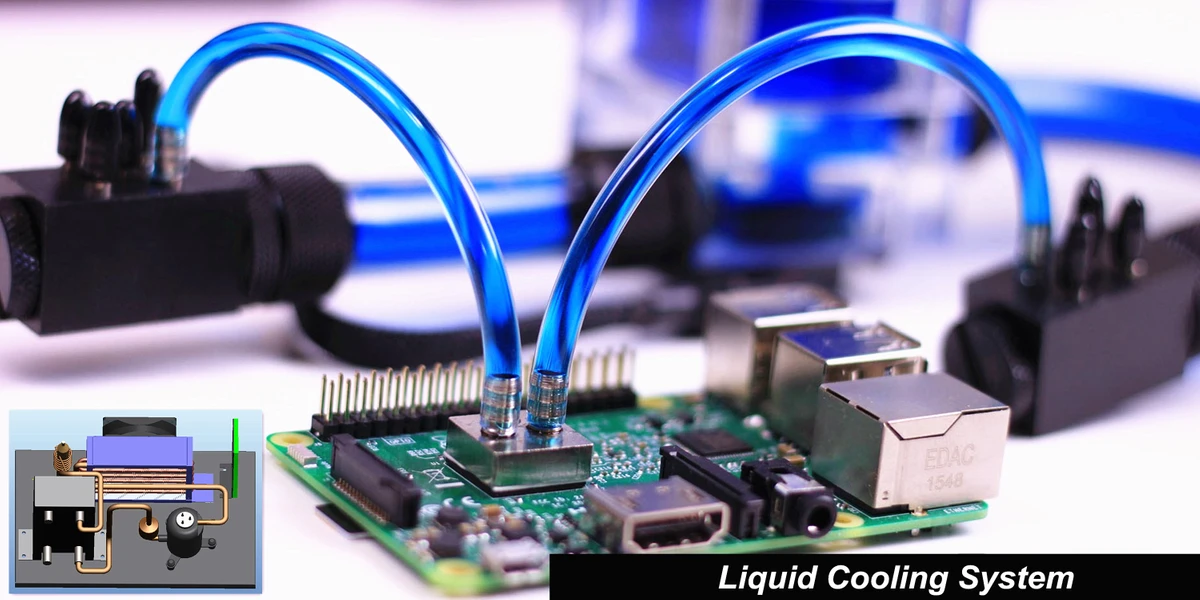
Electronics Cooling: Revolutionizing the Tech Industry
In today's fast-paced tech industry, the demand for efficient cooling solutions is higher than ever. Cold plates offer a highly effective method for dissipating heat from electronic components. By utilizing the principles of thermal conductivity, cold plates transfer heat away from sensitive electronics, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. With the advancement of liquid cooling technology, cold plates have become an indispensable tool for keeping high-powered electronics running at peak efficiency.
With the increasing demand for smaller and more powerful electronic devices, efficient cooling solutions have never been more critical. Cold plates are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for use in a wide range of electronic applications. Their ability to dissipate heat quickly and effectively ensures that sensitive components remain at optimal operating temperatures, even in the most demanding environments. As technology advances, cold plates are poised to play an even greater role in revolutionizing the tech industry by enabling the development of increasingly powerful and compact electronic devices.
Medical and Scientific Equipment: Enhancing Precision and Efficiency
Precision and efficiency are paramount in medical and scientific equipment. Cold plates maintain stable temperatures within sensitive instruments such as laboratory analyzers and medical imaging devices. Cold plates ensure consistent performance and accuracy in critical applications by effectively dissipating heat through direct contact with a cooling fluid. This has led to the widespread adoption of cold plate technology across various scientific and medical fields, revolutionizing how these instruments operate.
Automotive and Aerospace: Optimizing Performance and Reliability
The automotive and aerospace industries rely heavily on advanced cooling solutions to optimize performance and ensure reliability in demanding environments. Cold plates have emerged as a key component in cooling systems for electric vehicle batteries, power electronics, avionics, and other critical components. Through their efficient heat dissipation capabilities, liquid-cooled cold plates help maintain safe operating temperatures in high-stress situations, enhancing vehicle performance and extending component lifespan.
Advancements and Innovations in Cold Plate Technology

RIGID's Cutting-Edge Cold Plate Solutions
RIGID, a dynamic player in the cooling technology industry, has made significant strides in developing cutting-edge cold plate solutions. With a focus on innovation and efficiency, RIGID's cold plates are designed to maximize heat dissipation and thermal conductivity, ensuring optimal performance in various applications.
Integration of IoT and Smart Monitoring Systems
In line with the latest technological advancements, RIGID has integrated IoT (Internet of Things) and smart monitoring systems into their cold plate solutions. This allows for real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and other crucial metrics, enabling proactive maintenance and troubleshooting to ensure uninterrupted operation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
RIGID is committed to sustainability and reducing environmental impact through their cold plate technology. Using eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs, RIGID's cold plates minimize carbon footprint while delivering exceptional cooling performance. This emphasis on sustainability aligns with the global push for greener technologies.
Installation and Maintenance of Cold Plates

Best Practices for Installation and Integration
Ensuring the effective installation and integration of cold plates is vital for achieving optimal thermal performance and system reliability. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Proper Alignment and Secure Mounting: To maximize thermal conductivity, ensure cold plates are accurately aligned and securely mounted. Misalignment or loose mounting can lead to inefficient heat transfer and potential system failures.
- Optimized Integration: Integrate cold plates into the system with attention to flow rate and pressure drop factors. Precision in these aspects helps maintain consistent cooling performance and avoids bottlenecks in the system.
- Material Compatibility: To prevent corrosion or degradation, select cold plate materials that are compatible with the system. Choosing materials with appropriate thermal conductivity and resistance to chemical reactions will enhance durability and performance.
- Thorough Testing and Validation: Conduct comprehensive testing and validation to ensure the cold plate system performs efficiently. This includes checking for leaks, verifying temperature uniformity, and ensuring proper heat dissipation.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Implement a proactive maintenance schedule to inspect the cold plate system regularly. Early identification of potential issues can prevent costly downtime and extend the system's lifespan.
Adhering to these best practices—ensuring precise installation, choosing compatible materials, and maintaining a regular inspection routine—can optimize the performance and longevity of your cold plate systems, ultimately maximizing your investment and operational efficiency.
Proper Maintenance and Longevity of Cold Plate Systems
Regular cleaning and inspection are essential to maintaining the longevity of cold plate systems. This includes removing any debris or buildup that could impede heat transfer and checking for leaks or corrosion. Additionally, monitoring fluid levels and ensuring proper coolant circulation are vital for the overall functionality of the cold plate system. It is also important to regularly check the electrical connections and wiring to ensure they are secure and free from damage. Any loose connections or frayed wires can lead to inefficiencies or malfunctions in the system.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When cold plates experience common issues, such as inadequate cooling or uneven temperature distribution, troubleshooting may involve assessing the fluid flow rate, checking for blockages, or inspecting the integrity of the cold plate itself. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly is key to preventing potential damage to electronic components or other sensitive equipment.
After addressing the immediate troubleshooting steps, it is important to consider the long-term maintenance of cold plate technology. Regular cleaning and maintenance schedules can help prevent issues from arising. Additionally, investing in high-quality materials and components for cold plates can contribute to their overall reliability and performance. By staying proactive in the care and upkeep of cold plate systems, businesses can ensure that their electronic components and sensitive equipment remain well-protected.
The Future of Cold Plate Technology

Predictions and Projections for Cold Plate Development
As technology advances, the future of cold plate technology looks promising. We can expect to see even more efficient and compact cold plate designs with ongoing research and development. These advancements will likely focus on improving thermal conductivity and heat dissipation and enhancing the overall performance of cold plate systems.
Emerging Trends and Market Growth
The market for cold plates is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for electronics cooling solutions in various industries. As more companies recognize the benefits of liquid cooling over air cooling, the adoption of cold plate technology is expected to rise significantly. Additionally, emerging trends such as integrating IoT and smart monitoring systems will further propel market growth.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
While there are exciting opportunities in the future of cold plate technology, there are also potential challenges to consider. One key challenge is ensuring sustainability and minimizing environmental impact as demand for cold plates increases. However, this challenge also presents an opportunity for innovation in eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs that align with global sustainability goals.
RIGID's commitment to innovation positions us at the forefront of these emerging trends in cold plate technology. Our agile approach enables us to adapt quickly to market demands while focusing on sustainability and environmental responsibility. As we look ahead, RIGID remains dedicated to providing cutting-edge solutions that drive progress in cooling technology while meeting the evolving needs of our clients.
Remember that RIGID isn't a century-old company. Still, we move quickly and are unafraid to take responsibility. We focus on clients' budgets and take necessary steps to boost their competitiveness by working directly with customers to provide custom-made refrigeration solutions that meet their specific requirements.
RIGID: Your Partner for Innovative Cold Plate Solutions
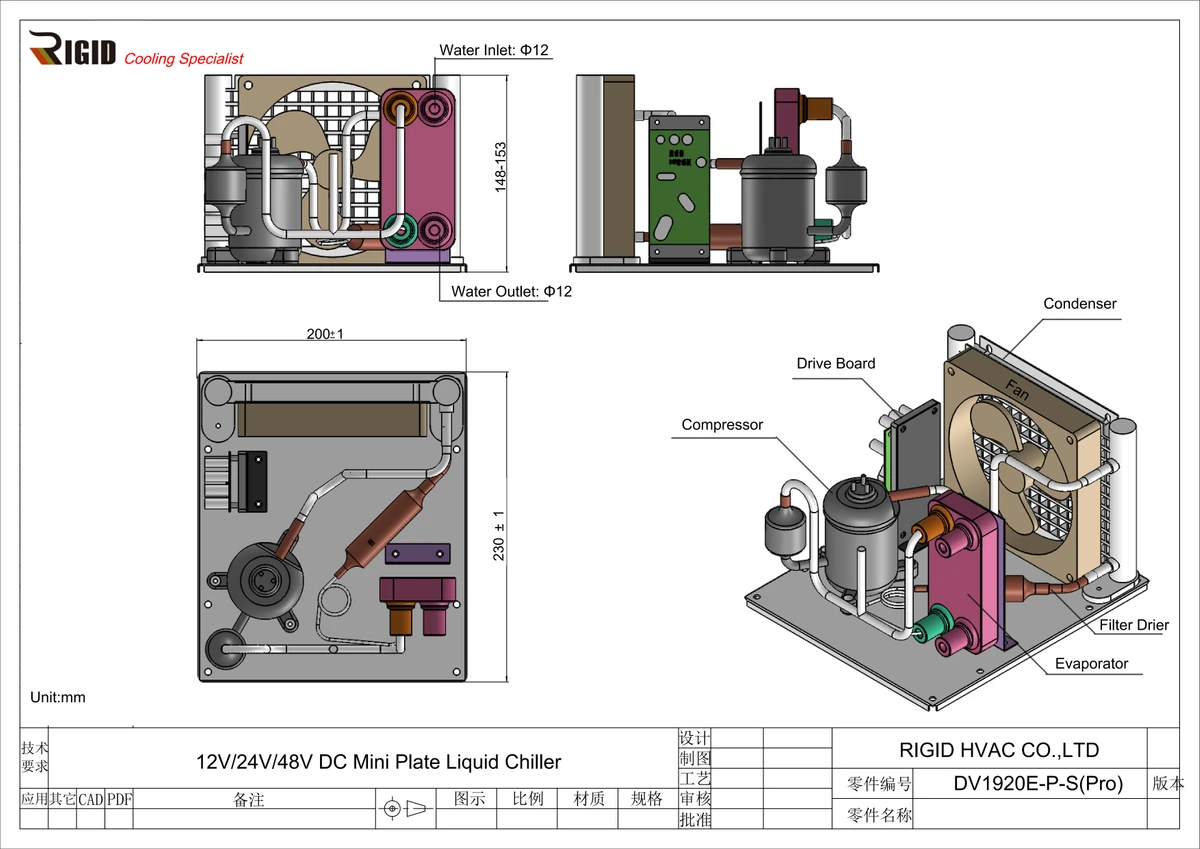
Maximizing Efficiency with Cold Plates: A Look Ahead
As the demand for efficient cooling solutions continues to grow, cold plates are poised to play a pivotal role in the future of thermal management. With advancements in materials and design, cold plates will become even more effective at dissipating heat and maintaining optimal temperatures in various applications. This will lead to increased energy efficiency and reduced operational costs, making cold plates an indispensable tool for industries across the board.
Investing in the Future of Cooling Technology
Investing in developing and implementing cold plate technology is a strategic move for businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve. As the global push for sustainability and energy efficiency gains momentum, cold plates offer a sustainable cooling solution that aligns with these goals. By investing in cutting-edge cold plate solutions, companies can enhance their operational efficiency and contribute to a greener future.
RIGID is at the forefront of innovative cooling technology, offering advanced cold plate solutions that cater to diverse industry needs. With a focus on customization and client collaboration, RIGID ensures that each customer receives tailored refrigeration solutions that align with their requirements and budget constraints. By partnering with RIGID, businesses can leverage state-of-the-art cold plate technology to optimize performance and reliability while staying competitive in their respective markets.
By embracing the potential of cold plates and staying abreast of emerging trends and innovations in this field, businesses can position themselves as leaders in efficient thermal management while contributing to environmental sustainability. With RIGID as your partner for innovative cold plate solutions, you can confidently navigate the evolving landscape of cooling technology and drive your business toward enhanced performance and success.