Introduction

In the world of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), understanding the basics is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their indoor climate. At the heart of any efficient air conditioning system are two key players: the compressor and condenser. These components work tirelessly in tandem within an AC unit, ensuring that your environment remains comfortable regardless of external conditions.
Understanding HVAC Basics
HVAC systems are designed to regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality in residential and commercial spaces alike. The effectiveness of these systems hinges on various components, with the compressor and condenser being among the most vital. Familiarizing yourself with how these elements function can empower you to make informed decisions about your HVAC needs.
The Role of Cooling Components
Cooling components like the compressor and condenser play a pivotal role in maintaining a stable indoor climate by removing heat from the air inside a building. The compressor acts as a pump that circulates refrigerant through the system, while the condenser dissipates heat outside. Together, they form an integral part of any AC unit's operation, contributing significantly to overall energy efficiency.
Overview of Compressor and Condenser
The compressor compresses refrigerant gas into a high-pressure state before sending it to the condenser for cooling down. This process is essential for converting low-temperature refrigerant back into liquid form so it can absorb more heat from indoors later on. In essence, understanding how both the compressor and condenser function will enhance your grasp of how an air conditioning system achieves its cooling effect.
What is a Compressor?

A compressor is a vital component of an air conditioning system, playing a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle that cools indoor spaces. Essentially, the compressor acts as the heart of an AC unit, pumping refrigerant through the system to facilitate heat exchange. By compressing low-pressure refrigerant gas into high-pressure gas, it enables efficient heat removal from your living environment.
Function in an AC Unit
In an air conditioning unit, the compressor's primary function is to increase the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant before it moves to the condenser. This process is essential because it allows the refrigerant to release absorbed heat outside, thereby cooling your home or office effectively. Without a properly functioning AC compressor, the entire air conditioning system would struggle to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
The compressor not only facilitates this heat transfer but also ensures that the refrigerant circulates efficiently throughout the HVAC system. By maintaining optimal pressure levels, it helps prevent potential breakdowns and inefficiencies that can lead to increased energy consumption. In summary, understanding how an AC compressor operates is key to appreciating its integral role in any air conditioning setup.
Types of Compressors
There are several types of compressors used in air conditioning systems today, each designed for specific applications and efficiency levels. The most common types include reciprocating compressors, scroll compressors, and rotary compressors—each with its unique mechanisms and benefits for HVAC systems. For instance, while reciprocating compressors are known for their reliability and effectiveness in smaller units, scroll compressors offer quieter operation and higher efficiency for larger applications.
Moreover, variable speed compressors have gained popularity due to their ability to adjust output based on cooling demand effectively. This flexibility leads to improved energy efficiency and reduced wear on components over time—a major plus for any homeowner or business owner looking to save on utility bills while maintaining comfort. Understanding these different types helps you make informed decisions when selecting an AC unit or condenser for your specific needs.
RIGID's Innovations in Compressors
RIGID has made significant strides in developing innovative compressor technologies that enhance performance while reducing energy consumption across various HVAC systems. Their commitment to research and development has led them to create advanced models featuring enhanced durability and quieter operation compared to traditional designs—perfect for residential or commercial settings where noise reduction is paramount.
Additionally, RIGID's focus on integrating smart technologies into their AC compressors allows users greater control over their air conditioning systems via mobile apps or smart home devices. This not only improves user experience but also promotes more efficient use of energy by allowing real-time adjustments based on occupancy patterns or external weather conditions.
In summary, RIGID's innovations stand out by combining cutting-edge technology with user-friendly features that cater specifically to modern-day expectations from both residential homeowners and commercial enterprises alike.
What is a Condenser?

In the realm of air conditioning systems, the condenser plays a pivotal role, working hand-in-hand with the compressor to ensure optimal cooling. As part of the AC unit, this component is responsible for dissipating heat absorbed by the refrigerant from inside your home to the outside environment. By doing so, it helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature while enhancing the overall efficiency of HVAC systems.
Role in the Air Conditioning System
The condenser's primary function is to convert refrigerant gas back into a liquid state after it has absorbed heat from your living space. When hot refrigerant enters the condenser from the compressor, it releases its heat as air passes over its coils, allowing cooler liquid refrigerant to flow back into the evaporator coil and continue the cooling cycle. This crucial process not only aids in regulating indoor temperatures but also ensures that your air conditioning system operates efficiently and effectively.
Components of a Condenser
A typical condenser consists of several key components that work together seamlessly within an AC unit. These include condenser coils, which are responsible for heat exchange; fans that help circulate air; and a casing that protects these elements from external environmental factors. Understanding these components can shed light on how a well-designed condenser contributes to improving HVAC performance.
RIGID’s Approach to Condenser Design
RIGID takes pride in its innovative approach to condenser design by focusing on efficiency and durability in their products. Their condensers are engineered using advanced materials and technologies that enhance heat transfer capabilities while minimizing energy consumption—perfect for those looking for high-performance HVAC solutions. With RIGID's custom solutions tailored specifically for various applications, you can trust their condensers will work harmoniously with your compressor and condenser setup for optimal results.
How They Work Together

Understanding how the compressor and condenser work together is crucial for grasping the overall functionality of an air conditioning system. These two components are like the dynamic duo of an AC unit, each playing a pivotal role in ensuring that cool air flows efficiently throughout your space. When they operate in harmony, they not only enhance comfort but also contribute to energy savings.
Process Flow in AC Units
In an air conditioning system, the process flow begins with the compressor, which takes low-pressure refrigerant gas and compresses it into high-pressure gas. This pressurized gas then travels to the condenser, where it releases heat and transforms into a liquid state. The cycle continues as this liquid refrigerant moves back to the evaporator, completing the loop that cools your environment.
Interaction Between Compressor and Condenser
The interaction between the compressor and condenser is vital for maintaining optimal performance in an AC unit. As the compressor pumps out high-pressure gas, the condenser dissipates heat from this gas to convert it into a liquid form effectively. This seamless exchange ensures that your air conditioning system operates smoothly while maximizing cooling efficiency.
Importance of Efficiency in HVAC Systems
Efficiency is paramount when it comes to HVAC systems; a well-coordinated operation between compressor and condenser can significantly impact energy consumption and costs. An efficient AC compressor paired with a well-designed condenser will not only keep your space comfortable but also reduce wear on components, extending their lifespan. Ultimately, investing in quality components leads to long-term savings and improved performance for any air conditioning setup.
Key Differences Between Compressor and Condenser

Design and Structure Variations
The design of a compressor and condenser reflects their unique functions within an air conditioning system. An AC compressor typically has a cylindrical shape, housing a motor that compresses refrigerant gas, while the condenser often appears as a flat or rectangular unit designed for heat exchange. These structural differences highlight how each component interacts with refrigerants: compressors manage pressure changes while condensers facilitate heat dissipation.
Moreover, compressors are usually built with robust materials to withstand high pressures during operation, whereas condensers utilize finned coils to maximize surface area for efficient heat transfer. This difference in design not only affects their physical appearance but also their installation requirements within an AC unit. Understanding these variations is essential when selecting components for your HVAC system.
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics serve as benchmarks for evaluating how well a compressor or condenser operates within an air conditioning system. For compressors, key metrics include energy efficiency ratio (EER) and coefficient of performance (COP), which indicate how effectively they convert electrical energy into cooling power. On the other hand, condensers are often assessed based on their ability to reject heat efficiently, measured through metrics like heat rejection capacity and airflow rates.
These performance indicators directly impact the overall efficiency of your AC unit; a high-performing compressor ensures effective refrigerant circulation while an efficient condenser enhances heat removal from the system. When comparing HVAC components, it's vital to consider these metrics since they can significantly influence energy consumption and operating costs over time.
Application Scenarios
The application scenarios for compressors and condensers vary greatly depending on specific needs in air conditioning systems. Compressors are commonly found in various types of AC units—ranging from residential split systems to large commercial chillers—where they play a critical role in maintaining desired temperature levels indoors. In contrast, condensers are often tailored for specific applications such as rooftop units or outdoor installations where effective heat exchange is paramount.
Moreover, choosing between different types of compressors—like rotary or scroll—depends on factors such as space constraints and noise levels in residential settings versus industrial environments where larger capacities may be required from condensers. By understanding these application scenarios better, you can make informed decisions when selecting components that best fit your HVAC needs.
Choosing the Right Components

Factors to Consider for HVAC Systems
Several factors come into play when selecting a compressor or condenser for your air conditioning system. First, you need to assess the size of your AC unit; an oversized or undersized component can lead to inefficiency and increased energy costs. Additionally, consider the climate in which you live—some compressors are designed for extreme temperatures, while others excel in milder conditions.
Another important aspect is energy efficiency ratings; look for models with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings that indicate better performance over time. The compatibility of the compressor and condenser with existing systems should also be evaluated, ensuring they can work together seamlessly within your HVAC setup. Lastly, don't forget about maintenance requirements; easier-to-service units can save you time and money down the line.
Benefits of Quality Compressors and Condensers
Investing in quality compressors and condensers pays off in numerous ways that extend beyond just immediate performance improvements. High-quality components tend to have longer lifespans, reducing the frequency of replacements and repairs—nobody enjoys dealing with a malfunctioning AC unit on a hot summer day! Moreover, reliable parts often operate more efficiently, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
A well-designed compressor will compress refrigerant effectively while minimizing noise levels—a quieter operation means a more pleasant indoor environment. Similarly, a robust condenser ensures proper heat exchange without overheating or causing system strain. Ultimately, quality components contribute significantly to the overall reliability of your air conditioning system.
RIGID's Custom Solutions for Your Needs
RIGID stands out by offering custom solutions tailored specifically for your HVAC needs; they understand that one size does not fit all when it comes to compressors and condensers. With an array of options available—ranging from high-efficiency AC compressors to innovative condensers designed for maximum airflow—you'll find exactly what suits your air conditioning system perfectly. RIGID's commitment to innovation means you're not just getting standard products; you're investing in cutting-edge technology that enhances performance.
Their team collaborates closely with clients during the selection process, ensuring that every aspect—from design specifications to application scenarios—is taken into account before making recommendations. This level of personalization guarantees that you'll receive components optimized for both efficiency and longevity within your specific environment. In short, RIGID makes it easy to choose quality components that elevate your HVAC experience.
Conclusion
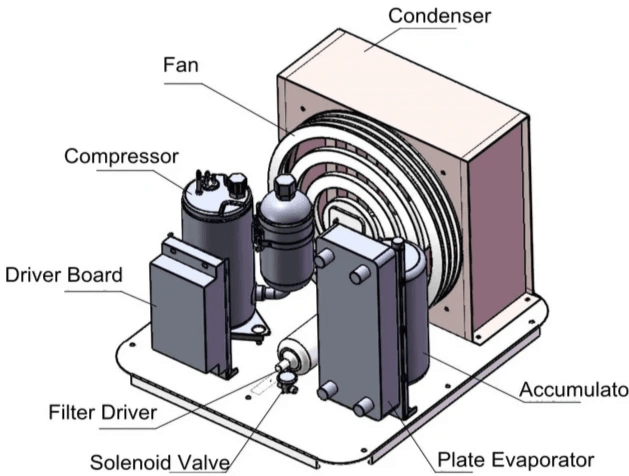
In the intricate world of HVAC systems, understanding the key components like the compressor and condenser is vital for anyone looking to optimize their air conditioning system. These elements not only work in tandem to ensure that your AC unit functions efficiently but also play a significant role in enhancing overall comfort levels in your space. By grasping how these components interact, you can make informed decisions about your air conditioning needs.
Importance of Understanding Key Components
Having a solid understanding of the compressor and condenser can significantly impact the performance of your air conditioning system. When you know how each piece contributes to cooling, you can better appreciate why investing in quality components matters. It’s not just about staying cool; it’s about ensuring that every part of your AC unit works harmoniously for maximum efficiency.
Impact on Air Conditioning Efficiency
The efficiency of an air conditioning system hinges largely on the performance of its compressor and condenser. A well-functioning AC compressor compresses refrigerant effectively, while an efficient condenser dissipates heat seamlessly, leading to optimal cooling performance. When both components are operating at peak efficiency, energy consumption decreases, which translates into lower utility bills—a win-win situation for homeowners!
Cutting-Edge Innovations in Cooling Technology
Innovation is at the forefront of HVAC technology, and companies like RIGID are leading the charge with advancements in compressor and condenser design. These innovations focus on improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact without compromising performance in air conditioning systems. As technology evolves, so do our options for more sustainable and effective solutions—making it an exciting time to invest in modern AC units designed with cutting-edge features.